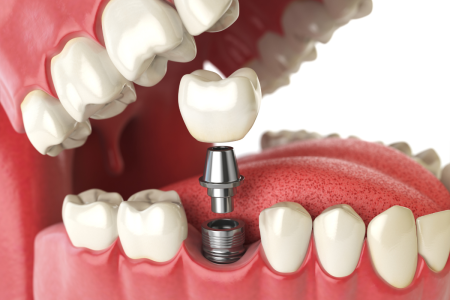
What is a stud bolt?
Stud screws for spines comprise of a completely strung steel bar and two weighty hexagonal steel nuts. Stud bolts are embedded in the spine openings and fixed to seal a flanged joint. The number, the length, and the measurement of the stud bolts expected for a flanged association rely upon the ribs type, breadth, and rating.
STUD BOLT AND NUTS
A stud bolt comprises of one strung steel pole and two (coordinating) hexagonal weighty steel nuts. Stud screws and nuts are fundamental parts of flanged joints, as they are vital to seal flanged joints appropriately.
Stud bolts are accessible in numerous distances across and lengths blends, metric and magnificent, and in an assortment of materials from carbon steel to amalgam, impeccable and nickel combinations (normal grades are: ASTM A193 B7, L7, B8, B8M, B16, Alloy 20, Monel, Hastelloy, Inconel, 17-4PH, titanium, and so forth.). These grades are talked about underneath in this article.
The material of the hex steel nuts will match the material of the strung bar (by and large, stud materials ASTM A193 coordinate with nuts materials ASTM A194).
The ASME B16.5 detail covers stud fasteners and nuts for ASME ribs (number, the distance across and the length of required stud screws, i.e “spine bolt outline”) by rib width, pressure class and face finish (RF, FF, RTJ).

A stud is a strung bar that is embedded into the openings of the mating spines and afterward fixed, at the two finishes, by applying a particular force to the steel nuts.
Stud bolt length (OAL/FTF)
The length of the stud can be estimated either as generally speaking length (i.e., “OAL”) or as “first useable string to first useable string” (i.e., “FTF”).
The FTF length can be determined by deducting a fourth of an inch to the OAL length, and it the standard stud length estimation for funneling applications.
Spines of various distance across and rating require stud of various lengths and measurements.
The stud is strung by the details set by ASME B1.1.
The expression “string pitch” alludes to the steepness of the point of string, which is estimated in strings per inch.
The most utilized string is the balanced string pitch type with a “V-profile” (a 60-degree point), as it is simpler for the maker to examine contrasted with the non-even sorts.
String series connect with the width and pitch mixes, estimated by the quantity of strings per inch (“TPI”) applied to a solitary breadth:
• Coarse string series (UNC/UNRC): UNC is the most well-known type for screws, fasteners, and nuts. Coarse strings are utilized for strings in low strength materials like iron, gentle steel, copper and milder combination, aluminum, and so on. The coarse string is additionally more open minded toward unfriendly circumstances and it works with fast get together
• Fine string series (UNF/UNRF): UNF is broadly utilized for accuracy obligations and when higher rigidity is required (versus the coarse string series)
• 8-Thread series (8UN) is the elective stringing technique for a few ASTM norms including A193 B7, A193 B8/B8M, and A320. This series is generally utilized for breadths from one inch upwards
Stud bolts covered by the ASTM A193 or A320 Specifications utilize 8UN for all measurements 1″ or more, and that intends that there are 8 strings for each inch for these sizes. For some other material grade, the purchaser will determine the string pitch except if it is given by the appropriate ASTM standard.
STUD BOLT MATERIALS
The most widely recognized materials for stud bolts (for ribs) are ASTM A193 (grade B7, B8, B8M, B8T), ASTM A453 (grade 660), ASTM A320 (grade L7, L7M), and ASTM A182 (duplex and very duplex blasting). For forceful liquids and conditions, stud bolts can be covered with Xylan, Xylar and different materials.
ASTM A193 STUD BOLTS (HIGH-TEMP.)
The ASTM A193 detail covers compound steel and hardened steel stud bolts materials for high temperature or high-pressure administration.
ASTM A193 stud bolts are accessible in public coarse (UNC) string pitches, by and large utilized in customary applications, and that actually intends that there are 8 strings for each inch (“string per inch”) for pole breadths over 1 inch. B7 is the most well-known determination grade for stud bolts.